Piston compressors are among the top choices for providing compressed air in various industries. But what makes this device so popular, and how can you choose the most suitable model for your requirements? TRYCOMP aims to explore the different types of piston compressors and share key tips for selecting the best model for your needs. This article serves as a guide to help you find the most suitable and cost-effective piston compressor for your industry.
What is a Piston Compressor, and How Does It Work?
A piston compressor is a device that compresses air using the back-and-forth movement of one or more pistons. In this process, air enters the cylinder through an intake valve. As the piston moves upward, the air pressure increases and is then discharged through an outlet valve. This simple yet efficient technology has made piston compressors a staple in many applications.
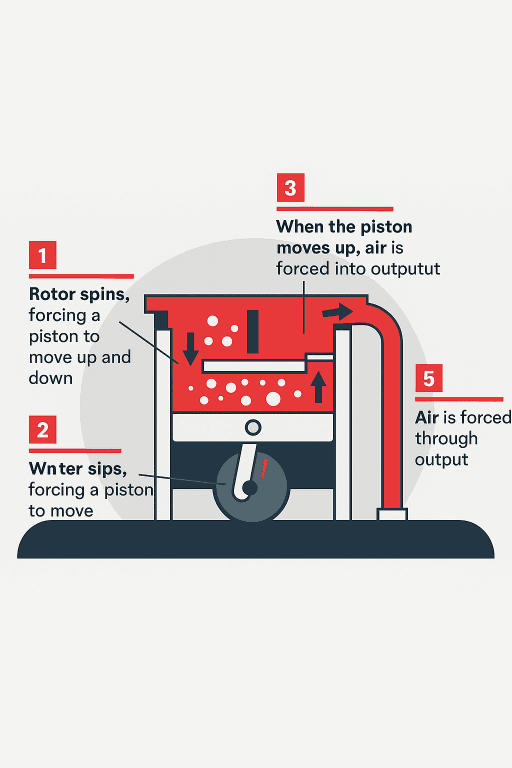
Types of Piston Compressors
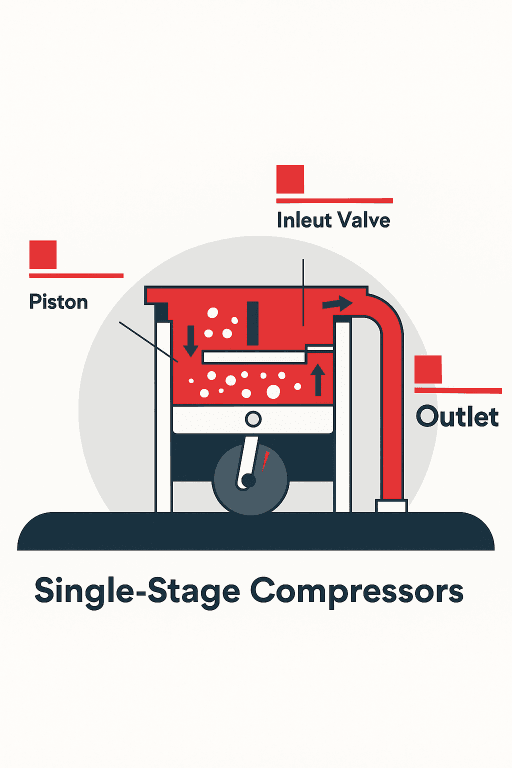
- Single-Stage Compressors: In these compressors, air is compressed only once. This model is suitable for applications requiring low to medium pressure. If you own a small workshop or use pneumatic tools, a single-stage piston compressor is ideal for your needs.
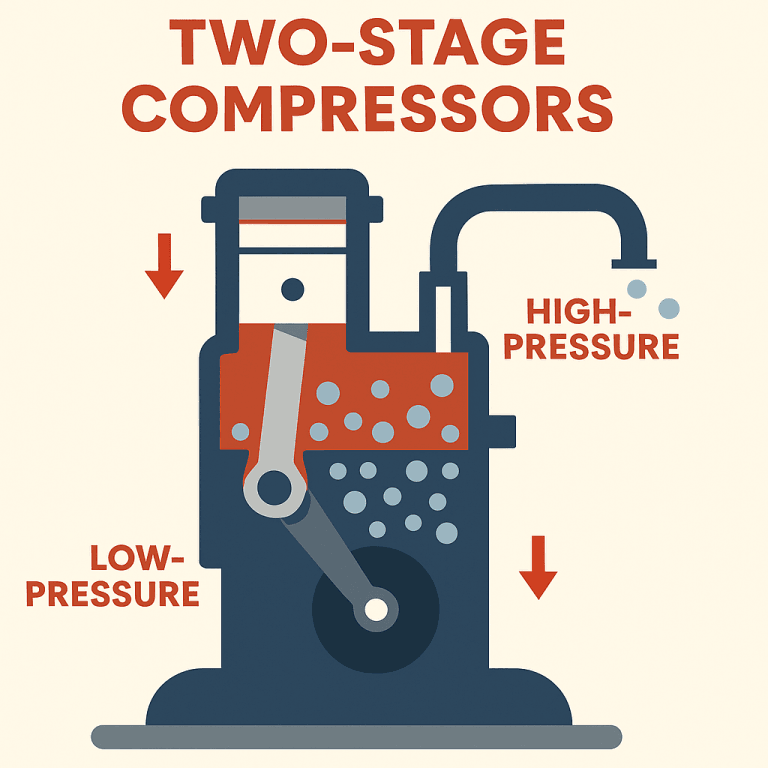
2. Two-Stage Compressors: These compressors compress air in two stages, enabling them to produce higher pressures. They are ideal for heavy-duty industries such as oil and gas, metallurgy, petrochemicals, cement production, marine industries, and power plants.
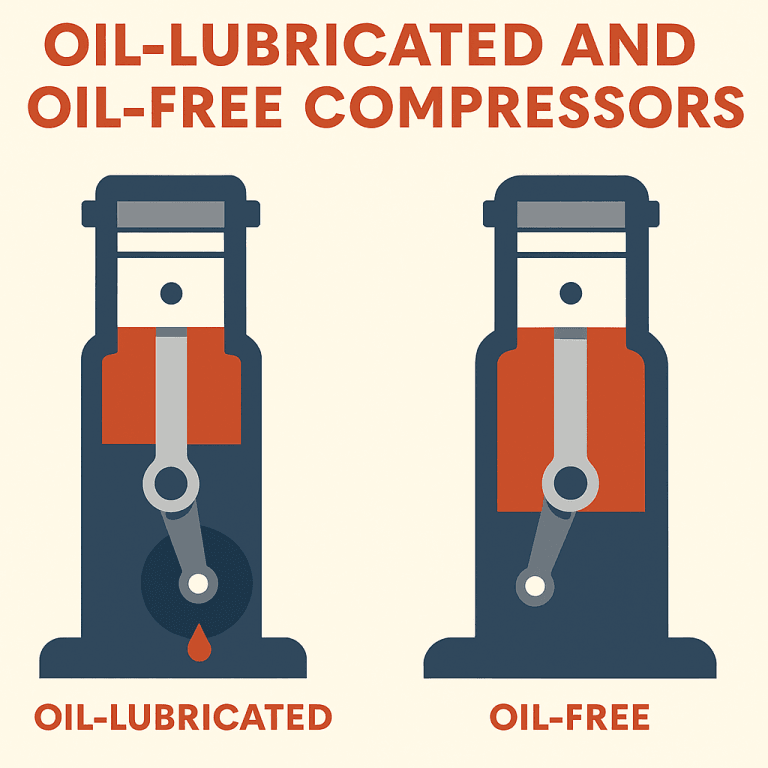
3. Oil-Lubricated and Oil-Free Compressors: Oil-lubricated compressors use oil to lubricate internal parts, offering greater durability. On the other hand, oil-free compressors are suitable for applications requiring completely clean air, such as in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
4. Stationary and Portable Compressors: Stationary compressors are commonly used in large industrial settings where the compressor’s location does not need to change. Portable compressors, due to their mobility, are ideal for construction projects or mobile applications.
Why Choose Piston Compressors? Pros and Cons
Advantages:
- Simple Construction: Piston compressors are easy to maintain and repair.
- Cost-Effective: The initial cost of a piston compressor is low, making it an economical option for various applications.
- High Pressure Capability: These compressors can handle high-pressure requirements, making them suitable for demanding processes.
- Versatile Applications: From small workshops to large industries, piston compressors offer flexible use.
Disadvantages:
- Noise Levels: Piston compressors are often noisy, which can be an issue in noise-sensitive environments.
- Energy Consumption: Compared to screw compressors, piston compressors have higher energy consumption and lower efficiency.
- Frequent Maintenance: They require regular maintenance, including oil changes and replacement of consumable parts.
A Guide to Buying a Piston Compressor
- Air Delivery Capacity (CFM): Ensure the compressor’s air delivery matches your requirements. For instance, if you use pneumatic tools or industrial processes, choose a compressor with an adequate capacity.
- Operating Pressure (PSI): Match the compressor’s pressure to your equipment’s specifications. For example, if your tools require 90 PSI, a compressor with 100 PSI would be suitable.
- Power Source: Electric compressors are ideal for environments with electricity access, while diesel or gasoline-powered models are better for remote areas without electricity.
- Cooling Method: Piston compressors can be air-cooled or water-cooled. For hot environments, water-cooled models are a better choice.
- Brand and Quality: Always buy from reputable brands to ensure quality and reliable after-sales service. TRYCOMP provides high-quality products and dependable support, making it a trusted choice for many customers.
Maintenance Tips for Your Compressor
- Routine Maintenance: Regularly change the oil, clean filters, and inspect mechanical parts to extend your compressor’s lifespan.
- Proper Environment: Avoid using compressors in high-temperature or excessively humid environments, which could damage the machine.
- Energy Efficiency: Opt for energy-efficient models to reduce operational costs.
FAQs About Piston Compressors
- Are piston compressors suitable for continuous use? No, piston compressors are designed for intermittent use. For continuous operations, screw compressors are a better choice.
- When should I change the oil in my compressor? The frequency depends on the type and model of the compressor, but typically oil should be replaced every 500 to 1,000 hours of operation.
- Which is better: single-stage or two-stage piston compressors? For low to medium pressure, single-stage models are sufficient. For higher pressure needs, two-stage models are recommended.
- Can I buy a second-hand piston compressor? Yes, but inspect the device thoroughly to ensure its parts are in good condition.
- Are piston compressors suitable for home use? Yes, small and portable models are perfect for home use and small workshops.
Why Choose TRYCOMP?
After reading this article, if you decide to purchase a piston compressor, TRYCOMP is the best choice for you. This brand offers high-quality products, excellent after-sales services, and expert consultations, ensuring a reliable and satisfying purchase experience. At TRYCOMP, we proudly provide a diverse range of piston compressors to meet the needs of various industries. For more information and to make a purchase, contact us today or visit the TRYCOMP website.

